The No Surprises Act (NSA) is the latest rule to increase transparency into medical billing. The goal is to reduce unexpected financial burden on patients when they have had no meaningful choice but to receive care from an Out-Of-Network (OON) Provider. This includes emergency and air ambulance services.
The NSA will prohibit balance billing and surprise billing by placing the administrative burden on insurance Payers to process these special cases. Both insurance Payers and healthcare Networks are preparing their workflows to comply with updates.
The highly technical nature of healthcare administrative processing benefits from the expertise of technology Providers ingrained in the industry, such as Smart Data Solutions. Even though the NSA presents monumental change, we’re all helping one another adapt together.
Our team’s preparation started with a shared understanding of the big players, key terminology, and important dates related to the NSA. We’ve summarized this below as a quick guide to the No Surprises Act for Payers and will update this post regularly as new information is released.
No Surprises Act: Terminology to Know
This list is a fast reference for the most popular organizations and terminology associated with the NSA.
Key Players
- Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) – The department responsible for creating the NSA with the mission of enhancing the health and well-being of all Americans.
- Office of Personnel Management (OPM) – The office serves as the chief human resources agency and personnel policy manager for the Federal Government.
Terminology
- Emergency services – This includes typical emergency services such as ambulance transports, air ambulance transports, services at an emergency facility, and post-stabilization care at an out-of-network facility. The NSA also applies to nonemergency care that’s performed by an out-of-network Provider at an in-network facility.
- Surprise Billing – This occurs when a patient receives a bill for an out-of-network service charge that they did not expect. A common scenario is having a procedure performed at an in-network facility, but an ancillary service specialist (e.g. anesthesiologist) is out-of-network.
- Balance Billing – This is when a patient is billed the remainder of an out-of-network medical charge that was negotiated by their insurer. For example, the Payer negotiates 20% of billed charges with the out-of-network Provider, and the Provider bills the patient the remaining 80%. The services do not fall under cost-sharing, such as a copay, coinsurance, or deductible.
- Qualified Payment Amount (QPA) – This is the median in-network contracted rate for similar services in a geographic region for the previous year, inflated by the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers. This is a key area in which partnering with SDS is beneficial because we pass along the QPA amount either in reporting or 837 segments, depending on which format you need.
- Advanced Explanation of Benefits (EOB) – An EOB-like document that provides estimated prices and cost-sharing details in advance of the scheduled treatment.
- Transparency in Coverage – This update requires Health Plans to publish the in-network negotiated rates, prescription drug prices, and the out-of-network billed and allowed amounts. Plans must publish this information on the web.
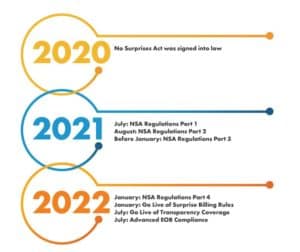
Important Deadlines
- Dec. 27, 2020 – the No Surprises Act was signed into law as part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (AHA)
- July 13, 2021 – HHS & OPM released “Requirements Related to Surprise Billing; Part I” which introduced the updated rule and set forth preparation for compliance.
- September 30, 2021 – HHS & OPM released an interim final rule, Part II (CMS) which expanded on the responsibilities of payers, providers, and patients.
- January 1, 2022 – This is the current deadline for NSA compliance. The rule will go into effect for healthcare Providers, facilities, and Providers of air ambulance services.
- Postponed to July 2022 – Compliance with Advanced EOB and Transparency in Coverage is postponed to July 2022 due to industry pushback. The concern is around slowing down turnaround times, the lack of a defined communication process, and potentially doubling the cost of processing a claim.
The No Surprises Act presents many challenges for teams who are responsible for administrative healthcare workflows. Fortunately, no one is alone with these changes. Payers can partner with technology companies such as Smart Data Solutions to create a custom plan for compliance with the NSA.
We are offering a free NSA consultation for Payers to help analyze their current workflows and recommend next steps specific to their business needs. Request your free consultation today to get ahead of the January 1, 2022 deadline for NSA compliance. Request a Consultation Here.

